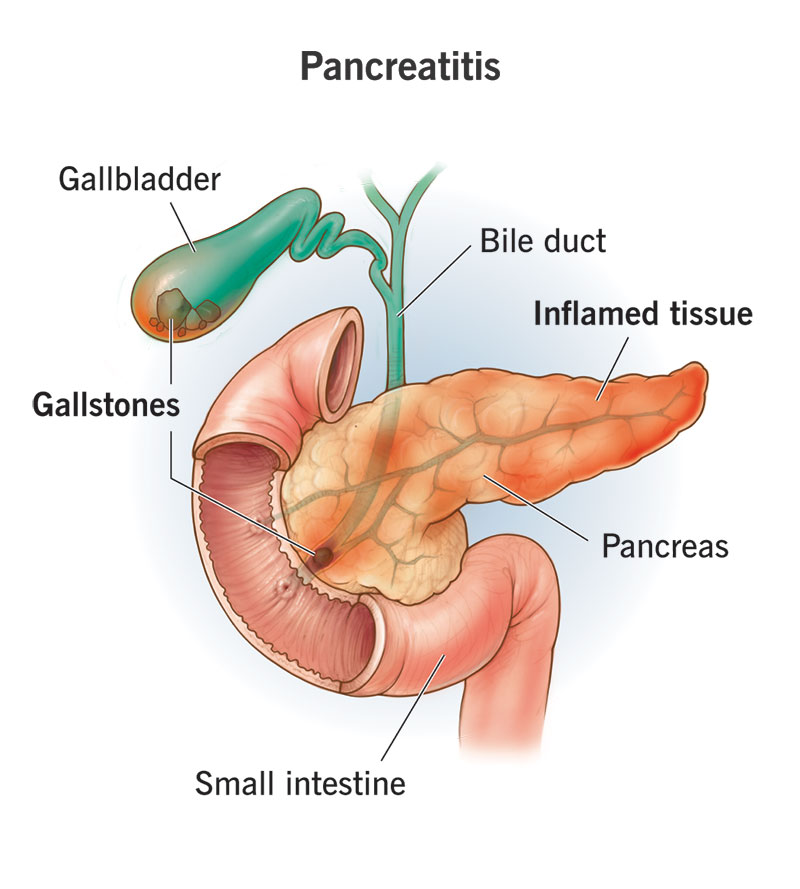
It is an uncontrolled cell division in the pancreas. Individuals with a habit of smoking, chronic alcoholism, and those having diabetes mellitus are at higher risk of developing cancer. The risk is also high in individuals with a family history of pancreatic cancer and hereditary pancreatitis.
Various diagnostic procedures are used to diagnose pancreatic cancer, such as:
Treatment depends on the stage of cancer and may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and/or surgery.
Decision making is part of a multidisciplinary team which A/Prof. Apostolou is a regular contributor and may chair at the Sydney Adventist Hospital.
Here a group of specialists including oncologists, surgeons and radiologists amongst others will discuss best practice options for treament of patients with this challenging problem.
Surgical Procedures
-
Whipple procedure:
This is the most common surgical procedure for cancer involving the head of the pancreas. In this procedure, the head of the pancreas, duodenum, gallbladder, and a portion of the stomach are removed. The gallbladder will also usually be removed at that time.
-
Distal subtotal pancreatectomy:
This surgical treatment is performed when the pancreatic cancer is in the body or tail of the pancreas. In this procedure, the body and tail of the pancreas, as well as the spleen, are removed. Appropriate immunisation is undertaken related to the splenectomy.